Misc Utilities¶
Getting Started¶
radial_distance¶
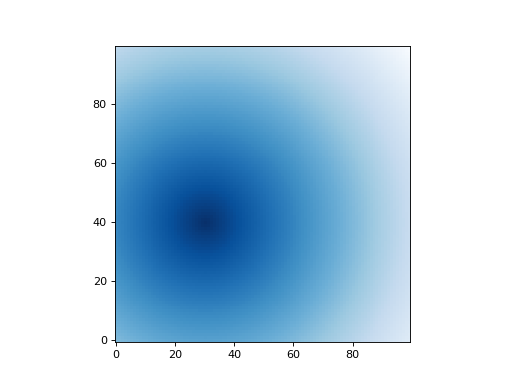
The radial_distance() function returns an
array where each value is the Euclidean distance from a given
position. In this simple example we set the origin position at (40,
30) ((y, x)) and get an array of shape (100, 100) ((ny,
nx)):
>>> from astroimtools import radial_distance
>>> data = radial_distance((40, 30), (100, 100))
Let’s plot the result:
>>> import matplotlib.pylab as plt
>>> plt.imshow(data, cmap='Blues_r', origin='lower',
... interpolation='nearest')
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf, svg)
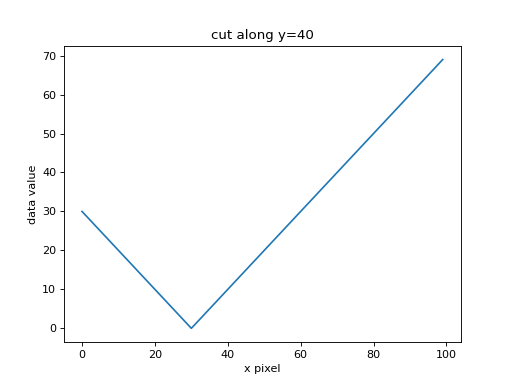
Here’s a cut along y=40 of the data array:
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf, svg)
listpixels¶
The listpixels() function returns an Astropy
Table listing the (y, x) positions and data
values for a subarray (or the entire array):
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from astroimtools import listpixels
>>> np.random.seed(12345)
>>> data = np.random.random((25, 25))
>>> tbl = listpixels(data, (8, 11), (3, 3))
>>> for col in tbl.colnames:
... tbl[col].info.format = '%.8g' # for consistent table output
>>> tbl.pprint(max_lines=-1)
x y value
--- --- -----------
10 7 0.75857204
11 7 0.069529666
12 7 0.70547344
10 8 0.8406625
11 8 0.46931469
12 8 0.56264343
10 9 0.034131584
11 9 0.23049655
12 9 0.22835371
listpixels also supports
NDData objects as input.
mask_databounds¶
The mask_databounds() function creates or
updates a mask by masking data values that are below a lower bound,
above an upper bound, equal to particular value, or are invalid (e.g.
np.nan or np.inf).
Here is a simple example of creating a mask array where data is less than 2, greater than 5, or equal to 3:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from astroimtools import mask_databounds
>>> data = np.arange(7)
>>> data
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
>>> mask_databounds(data, lower_bound=2, upper_bound=5, value=3)
array([ True, True, False, True, False, False, True]...)
If mask is input, then it will be updated:
>>> mask = [False, False, True, False, False, False, False]
>>> mask_databounds(data, mask=mask, lower_bound=2, upper_bound=5, value=3)
array([ True, True, True, True, False, False, True]...)
Additionally, invalid data values (e.g., NaN and inf) are masked if
mask_invalid is True (the default):
>>> data = np.arange(7.)
>>> data[2] = np.nan
>>> data
array([ 0., 1., nan, 3., 4., 5., 6.])
>>> mask_databounds(data, upper_bound=5, mask_invalid=True)
array([False, False, True, False, False, False, True]...)
nddata_cutout2d¶
The nddata_cutout2d() function creates a 2D
cutout of a 2D NDData object. Specifically, cutouts
will made for the nddata.data and nddata.mask (if present)
arrays. If nddata.wcs exists, then it will also be updated. Note
that cutouts will not be made for nddata.uncertainty (if present)
because they are general (unstandardized) objects and not arrays.
Let’s start by creating a simple NDData object with
units, a mask, and a meta dict:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from astropy.nddata import NDData
>>> import astropy.units as u
>>> from astroimtools import nddata_cutout2d
>>> data = np.random.random((500, 500))
>>> unit = u.electron / u.s
>>> mask = (data > 0.7)
>>> meta = {'exptime': 1234 * u.s}
>>> nddata = NDData(data, mask=mask, unit=unit, meta=meta)
Now let’s create a 2D cutout centered at (y, x) of (100, 100)
and with a shape of (10, 10) ((ny, nx)):
>>> cutout = nddata_cutout2d(nddata, (100, 100), (10, 10))
>>> cutout.data.shape
(10, 10)
>>> cutout.mask.shape
(10, 10)
>>> cutout.unit
Unit("electron / s")
Reference/API¶
Misc utility functions.
Functions¶
|
Return an array where each value is the Euclidean distance from a given position. |
|
Return a |
|
Create or update a mask by masking data values that are below a lower bound, above an upper bound, equal to particular value, or are invalid (e.g. np.nan or np.inf). |
|
Create a 2D cutout of a |